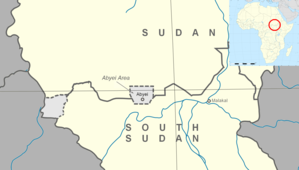
Abyei
Abyei Area
منطقة أبيي mintaqat 'abyi | |
|---|---|
| Abyei Area Administration | |
 Location | |
| Countries | |
| Comprehensive Peace Agreement | 9 January 2005 |
| Headquarters | Abyei Town |
| Government | |
| • Type | Abyei Area Administration |
| • Chief Administrator | Kuol Deim Kuol[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10,546 km2 (4,072 sq mi) |
| Population (2014) | |
| • Total | 124,390[citation needed] |
| Time zone | UTC+02:00 (CAT) |
The Abyei Area (Arabic: منطقة أبيي) is an area of 10,546 km2 or 4,072 sq mi[2] on the border between South Sudan and Sudan that has been accorded "special administrative status" by the 2004 Protocol on the Resolution of the Abyei Conflict (Abyei Protocol) in the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) that ended the Second Sudanese Civil War.[3] The capital of the Abyei Area is Abyei Town. Under the terms of the Abyei Protocol, the Abyei Area is considered, on an interim basis, to be simultaneously part of both the Republic of South Sudan and Republic of Sudan, effectively a condominium.
In contrast to the borders of the former district, the Abyei Protocol defined the Abyei Area as "the area of the nine Ngok Dinka chiefdoms transferred to Kordofan in 1905".[3] In 2005, a multinational border commission established this to be those portions of Kordofan south of 10°22′30″ N.[4] However, following continued disputes that erupted into violence and threatened the CPA, an international arbitration process redrew Abyei's boundaries in 2009 to make it significantly smaller, extending no further north than 10°10′00" N.[5] This revised border has now been endorsed by all parties to the dispute.[citation needed]
History[edit]
 |
|---|
|
|
 |
|---|
| Constitution |
The Sudan Tribune claims that the Dajo people were located in the region of Abyei prior to the seventeenth century, before being displaced by new migrants.[6] From at least the eighteenth century Abyei was inhabited by the agro-pastoralist Ngok Dinka, a sub-group of the Dinka of Southern Sudan. The Messiria, a nomadic Arab people, who spend most of the year around their base at Muglad in northern South Kurdufan, would graze their cattle south to the Bahr river basin in Abyei during the dry season.[7][8][9] Abyei's permanent residents were thus the southern Dinka, but half the year the Dinka were outnumbered by the Muslim, northern Misseriya.[10] At the establishment of the Anglo-Egyptian Condominium, the Messiria were predominantly located in the province of Kordofan (considered "northern"), while the Ngok Dinka were located in Bahr el Ghazal (considered "southern"). In 1905, after continued raids by the Messiria into Ngok Dinka territory, the British redistricted the nine Ngok Dinka chiefdoms into Kordofan. The reason was threefold: to protect the Ngok Dinka from raids by the Messiria and thus pacify the area; to demonstrate that a new sovereign power was in control; and to bring the two feuding tribes under common administration.[11] When the British left in 1956, they left the status of Abyei unclear.[10]
The two peoples began to take separate paths with the onset of the First Sudanese Civil War (1956–1972), in particular the 1965 massacre of 72 Ngok Dinka in the Misseriya town of Babanusa. The Ngok Dinka were thus drawn to the Anyanya, while the Messiria were favored by the Khartoum-based government and became firmly associated with the north. The 1972 Addis Ababa Agreement that ended the war included a clause that provided for a referendum allowing Abyei to choose to remain in the north or join the autonomous South. This referendum was never held and continued attacks against Ngok Dinka led to the creation of Ngok Dinka unit in the small Anyanya II rebellion, which began in Upper Nile in 1975. The discovery of oil in the area, among other north-south border regions, led President Gaafar Nimeiry to try the first of many initiatives to redistrict oil rich areas into northern administration.[8]
The Ngok Dinka unit of Anyanya II formed one of the foundations of the rebel movement at the beginning of the Second Civil War in 1983. Many Ngok Dinka joined the rebels upon the outbreak of hostilities. Partially as a result of their early entry into the war, many Ngok Dinka rose to leadership positions in the Sudan People’s Liberation Army (SPLA), becoming closely associated with John Garang. In contrast, the Messiria joined the hostilities on the side of the government in the mid-1980s. They formed frontline units as well as Murahleen, mounted raiders that attacked southern villages to loot valuables and slaves.[12] By the end of the war the intense fighting had displaced most Ngok Dinka out of Abyei, which the Misseriya state as justification for ownership of the area.[7]
Status dispute[edit]
Abyei Protocol in the Comprehensive Peace Agreement[edit]
The status of Abyei was one of the most contentious issues in the negotiation of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement. The first protocol signed, the 2002 Machakos Protocol, defined Southern Sudan as the area as of independence in 1956. It thus excluded the SPLA strongholds in Abyei, the Nuba Mountains and Blue Nile, known collectively during the talks as the Three Areas. The SPLA negotiators then spent several years attempting to give these regions the right to a referendum in which they could decide if they want to be under the administrative control of the north or south. This would potentially mean that these regions would become part of a nation of South Sudan after the 2011 independence referendum. The government blocked these attempts, stating that the Machakos Protocol had already delineated the border for the Three Areas in favor of the north.[13]
The deadlock was finally broken by pressure from the United States. U.S. presidential envoy John Danforth circulated a draft agreement, which the U.S. convinced the government to sign despite its inclusion of a referendum. The Protocol on the resolution of the Abyei conflict put Abyei into a special administrative status government directly by the presidency. The precise borders of the area were to be determined by an Abyei Borders Commission (ABC), followed by a referendum commission to identify Messiria that are resident in Abyei and could thus vote in local elections in 2009; all the Ngok Dinka were to be considered resident, it being their traditional homeland.
Abyei Borders Commission[edit]
According to an annex to the protocol adopted in December 2004, the Abyei Borders Commission was to be composed of 15 persons: five appointed by the government, five by the SPLA and three by the Intergovernmental Authority on Development, and one each by the United States and the United Kingdom. Only the five impartial experts could present the final report. The five appointed were: Godfrey Muriuki of the University of Nairobi; Kassahun Berhanu of the Addis Ababa University; Douglas H. Johnson, an author of several works on southern Sudan; Shadrack Gutto, a lawyer from South Africa; and Donald Petterson, a former ambassador to Sudan.[7] The ABC determined the boundary at approximately 10°22′30″N., 87 km (54 mi) north of the town of Abyei, following the agreed rules of procedure.[14] The process and the map showing the boundary is detailed by Johnson.[4]
The ABC presented their report to the president on 14 July 2005, whereupon it was immediately rejected by the government, who accused the experts of using sources after 1905 in their determination of the boundaries. The death of John Garang later that month pushed all other issues off the national agenda, but the SPLA maintains that the terms of the Abyei protocol must be held to.[15] Government resistance to an agreement is largely based on an attempt to hold on to the oil reserves and oil pipelines in the area.[16]
Renewed tensions and violence[edit]
In October 2007, rising tensions between the SPLA and government resulted in the SPLA temporarily withdrawing from the Government of National Unity over several deadlocked issues, notably Abyei.[17] At the time, the International Crisis Group stated, "What happens in Abyei is likely to determine whether Sudan consolidates the peace or returns to war".[18] Armed violence erupted in the Abyei region during late 2007 and throughout 2008. Clashes occurred both between the SPLA and Messiria fighters and between the SPLA and government troops.
Messiria leaders had objected to demarcation provisions of the CPA which they claim have a negative impact upon Messiria access to grazing lands. These grievances fed into armed clashes in December 2007, which killed at least 75 people, and further violence in February and March 2008, resulting in numerous deaths and civilian displacement. These clashes were considered by analysts to represent a serious threat to the peace process and trigger a resumption of civil war.[19][20][21][22][23][24] The Messiria were not believed to be directly controlled by Khartoum, however analysts pointed out that local disputes over resources are readily manipulated by outside forces.[25]
Following the violence of February and March, the Sudanese government deployed a contingent of 200 or more soldiers to Abyei town on 31 March 2008.[26] Armed clashes between these troops and the SPLA occurred during May 2008 resulting in dozens of deaths and the displacement of an estimated 25,000 civilians.[27][28][29][30] Much of Abyei town was razed; publicist Roger Winter stated that "the town of Abyei has ceased to exist".[31]
Arbitration by a panel under the Permanent Court of Arbitration[edit]
| Abyei Arbitration | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Court | Permanent Court of Arbitration |
| Full case name | The Government of Sudan v. The People's Liberation Movement/Army (Abyei Arbitration) |
| Decided | 22 July 2009 |
| Court membership | |
| Judges sitting | Professor Pierre-Marie Dupuy, president H.E. Judge Awn Al-Khasawneh Professor Dr. Gerhard Hafner Professor W. Michael Reisman Judge Stephen M. Schwebel |
| Case opinions | |
| Decision by | Unanimous panel |
Following the clashes in Abyei during May 2008, in June 2008 the Sudanese President, Omar al-Bashir, and the President of the autonomous Government of Southern Sudan, Salva Kiir Mayardit, agreed to refer the disputes between the Government and the SPLM/A concerning the ABC's determination of the Abyei area's boundaries to international arbitration at the Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA), in The Hague.[32]

The arbitration was presided over by an arbitral tribunal composed of five international lawyers – Professor Pierre-Marie Dupuy, of France, as President, with Judge Stephen M. Schwebel, Professor W. Michael Reisman, H.E. Judge Awn Al-Khasawneh and Professor Dr. Gerhard Hafner. The tribunal adopted the PCA's Optional Rules for Arbitrating Disputes Between Two Parties of Which Only One is a State.[33]
The SPLM/A appointed Dr. Riek Machar Teny, Deputy Chairman of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement and Minister Luka Biong Deng, as Agents, and Gary Born, Paul Williams and Wendy Miles as counsel. The Government of Sudan appointed Ambassador Dirdeiry Mohamed Ahmed as Agent, and were represented by Professor James Crawford QC, S.C., Dr Nabil Elaraby, Professor Alain Pellet, Rodman Bundy and Loretta Malintoppi.

Following extensive written pleadings,[34] in April 2009 the parties presented their closing submissions to the arbitration tribunal over six days at an oral hearing at the Peace Palace, The Hague. In a groundbreaking initiative, the parties agreed to broadcast the oral hearing over the internet, which allowed those in Sudan and around the world to see the parties put forward their arguments.[35] Following the hearing the arbitral tribunal then began its deliberations and, less than ninety days later, on 22 July 2009 rendered its final binding decision as to the validity of the boundaries for Abyei and the ABC had drawn.[36]
The award ordered the redrawing of the northern, eastern and western boundaries, thus decreasing the size of Abyei. The size of Abyei is crucial to the political dispute, as its residents will be able to vote in a referendum on whether to become part of northern or southern Sudan.[5][37] The redrawn borders give control of the richest oil fields in the Abyei region, such as the Heglig oil field, to the north, while giving at least one oil field to the south. Most of the Messiria are outside of the redrawn borders, making it far more likely that the region will vote to join the south. Announcements by both the SPLM and Government of Sudan that they would accept the ruling were hailed by the United States, European Union, and the United Nations.[38]
Leadup to referendum[edit]
As of December 2010, the PCA border has not been demarcated and there is still no agreement on who constitutes a "resident of Abyei" for the purposes of voting in the Abyei referendum. The question is whether to include Arab nomads (the Messiria tribe), who have historically stayed in the region every year for six months. If the Misseriya Arabs are prevented from voting, the region will likely go to South Sudan.[39] While the Dinka Ngok and Messiria tribe maintained a peaceful coexistence during the civil war, the division of Sudan has created mistrust between the two people.[40] In the second week of January 2011, when a referendum was held regarding South Sudanese independence, a simultaneous referendum to determine the fate of Abyei was meant to be held. This referendum was postponed due to the disagreement over voter eligibility.[10]
Takeover by north[edit]
On 21 May 2011 it was reported that the Armed Forces of Sudan had seized control of Abyei with a force of approximately 5,000 soldiers after three days of clashes with the South.[41] The precipitating factor was an ambush by the South killing 22 northern soldiers. The northern advance included shelling, aerial bombardment and numerous tanks.[42] Initial reports indicate that over 20,000 people have fled. The South Sudanese government has declared this as an "act of war", and the U.N. has sent an envoy to Khartoum to intervene.[41] South Sudan says it has withdrawn its forces from Abyei.[43]
As of May 2011, the prospective referendum on Abyei's future status has been postponed indefinitely.[44] The northern leader, then President al-Bashir, dismissed the southern chief administrator of Abyei and appointed a northerner, Ahmed Hussein Al-Imam.[42][45]
Protests[edit]
Protests were held in at least two Southern states, Upper Nile and Warrap, over the occupation of Abyei by Northern forces. Labor leader Abraham Sebit, leading the protest in Malakal, Upper Nile, asked for intervention by the United Nations and suggested a no-fly zone could be established over Abyei.[46] Governor Nyadeng Malek of Warrap also condemned the occupation.[47]
Ceasefire and enforcement[edit]
A deal on demilitarization was reached on 20 June 2011.[48] The United Nations Interim Security Force for Abyei, consisting of Ethiopian troops commanded by Lieutenant General Tadesse Werede Tesfay, were to be deployed under a UNSC resolution from 27 June 2011.[49]
The peacekeepers began arriving in Abyei on 15 July 2011 after traveling overland from Ethiopia, just under a week after South Sudan formally declared its independence. Both countries continue to claim Abyei, but the presence of the Ethiopians is intended to prevent the military of either from attempting to wrest control of it.[50][51][52][53]
Abyei Area Administration[edit]
Under the terms of the Abyei Protocol, the residents of the Abyei Area have been declared, on an interim basis, to be simultaneously citizens of the states of West Kurdufan (Republic of Sudan) and Northern Bahr el Ghazal (South Sudan) until such time as a referendum can determine the permanent status of the area. An Abyei Area Administration was established on 31 August 2008.
Structure[edit]
The Abyei Area Administration is made up of the following bodies:[54][55]
- An Executive Council led by a Chief Administrator representing the SPLM and a Deputy Chief Administrator representing the Government of Sudan. The remaining members will be shared between the two entities with SPLM nominating three and the GOS nominating two.
- The Abyei Joint Oversight Committee made up of two members representing each party to the agreement.
- The Abyei Area Security Committee composed of the Chief Administrator, Deputy Chief Administrator, an armed forces commander, the local police chief, and a representative of the "security organ".
A United Nations peacekeeping mission, the United Nations Interim Security Force for Abyei, has also been established to protect civilians and humanitarian workers in the Abyei Area.
The administrative name was changed to "Abyei Special Administrative Area" in July 2015 with the administration stating that it won't share the region again with Sudan.[56]
Chief Administrators[edit]
| Tenure | Incumbent | Party |
|---|---|---|
| 31 August 2008 – 30 December 2009 | Arop Moyak | SPLM |
| 30 December 2009 – 21 May 2013[citation needed] | Deng Arop Kuol | SPLM |
| May 2013[citation needed] – March 2015 | Kuol Monyluak Dak[57] | SPLM |
| March 2015 – February 2017 | Dr. Chol Deng Alak[45][58] | SPLM |
| February 2017 – June 2020 | Kuol Alor Kuol Arop (Kuol Alor Jok)[59] | SPLM |
| June 2020 – present | Kuol Deim Kuol[60] | SPLM |
Towns and villages[edit]
- Abyei Town
- Agok
- Al Malamm
- Awolnhom
- Bargnop
- Dokura
- Fyok
- Lukji
- Mokwei
- Umm Geren
- Makhir Abior
- Amiet
- Lou
- Kolom
Oil reserves and production[edit]
Abyei is situated within the Muglad Basin, a large rift basin which contains a number of hydrocarbon accumulations. Oil exploration was undertaken in Sudan in the 1970s and 1980s. A period of significant investment in Sudan’s oil industry occurred in the 1990s and Abyei became a target for this investment. By 2003 Abyei contributed more than one quarter of Sudan’s total crude oil output. Production volumes have since declined[61] and reports suggest that Abyei’s reserves are nearing depletion. An important oil pipeline, the Greater Nile Oil Pipeline, travels through the Abyei area from the Heglig and Unity oil fields to Port Sudan on the Red Sea via Khartoum. The pipeline is vital to Sudan’s oil exports which have boomed since the pipeline commenced operation in 1999.[62][63]
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ Abyei chief administrator appoints new cabinet
- ^ GETTLEMAN, JEFFREY (25 May 2011). "U.N. Warns of Ethnic Cleansing in Sudan Town". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
- ^ a b “Protocol on the resolution of Abyei conflict”, Government of the Republic of Sudan and the Sudan People’s Liberation Movement/Army, 26 May 2004 (hosted by reliefweb.int)
- ^ a b “Why Abyei Matters”, African Affairs, 107/426, 1–19, 23 December 2007
- ^ a b "The Government of Sudan / The Sudan People's Liberation Movement/Army (Abyei Arbitration)". Permanent Court of Arbitration. Archived from the original on 20 November 2011. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Abyei Issue from a neutral perspective". Sudan Tribune. 25 November 2007. Archived from the original on 26 July 2009. Retrieved 23 July 2009.
- ^ a b c “Resolving the Boundary Dispute in Sudan’s Abyei Region” Archived 15 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine by Dorina Bekoe, Kelly Campbell and Nicholas Howenstein, United States Institute of Peace, October 2005
- ^ a b "Sudan: Breaking the Abyei Deadlock". Archived from the original on 9 February 2011. Retrieved 30 May 2011. (456 KB), International Crisis Group, 12 October 2007, p. 2
- ^ "GOS-SPLM/A Final Award" (PDF). Permanent Court of Arbitration. 22 July 2009. pp. 36–37. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 August 2009. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ a b c "Collapse of a Country: A Diplomat's Memoir of South Sudan." By Nicholas Coghlan. McGill-Queen's University Press, 2017.
- ^ Permanent Court of Arbitration, the Hague "On Delimiting Abyei" Archived 6 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine 22 July 2009 / p221-222
- ^ "Sudan: Breaking the Abyei Deadlock", pp. 2–3
- ^ "Sudan: Breaking the Abyei Deadlock", p. 3
- ^ “The Abyei Protocol Demystified” Archived 11 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine, Sudan Tribune,11 December 2007
- ^ "Sudan: Breaking the Abyei Deadlock", p. 4
- ^ "Sudan: Breaking the Abyei Deadlock", p. 9
- ^ “SUDAN: Southern leaders in talks to salvage unity government”, IRIN, 18 October 2007
- ^ "Sudan: Breaking the Abyei Deadlock", p. 11
- ^ Wheeler, S. 2008, ‘Armed Sudanese nomads block key north-south route’, Reuters Africa, 12 February. Retrieved 11 March 2008.
- ^ IRIN 2008, ‘SUDAN: War of words after scores killed in Abyei’, IRIN, 3 March. Retrieved 4 March 2008.
- ^ BBC 2008, ‘Arab nomads dead in Sudan clashes’, BBC News, 2 March. Retrieved 4 March 2008.
- ^ Shahine, A. 2008, ‘Sudan nomads clash with ex-rebels, dozens killed’, Reuters AlertNet, 2 March. Retrieved 4 March 2008.
- ^ Sudan Tribune 2008, ‘Fresh fighting breaks out in Sudan north-south region’, Sudan Tribune, 22 March. Retrieved 22 March 2008.
- ^ IRIN 2008, ‘SUDAN: Rising tension in Abyei as clashes displace hundreds’, IRIN, 24 March. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ Kilner, D. 2008, ‘Clashes on Sudan’s North-South border threaten peace deal’ Archived 15 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Voice of America, 10 March. Retrieved 10 March 2008.
- ^ Wheeler, S. 2008, ‘Northern troops enter disputed Sudan oil town’, Reuters AlertNet, 2 April. Retrieved 4 April 2008.
- ^ Al Jazeera 2008, ‘Many dead in Sudan clashes’, Al Jazeera English, 16 May. Retrieved 17 May 2008.
- ^ IRIN 2008, ‘SUDAN: Abyei town deserted after fresh clashes’, IRIN, 16 May. Retrieved 17 May 2008.
- ^ BBC 2008, ‘Fighting in disputed Sudan town’, BBC News, 20 May. Retrieved 20 May 2008.
- ^ BBC 2008, ‘Tensions flare in central Sudan’, BBC News, 24 May. Retrieved 26 May 2008.
- ^ Winter, R. 2008, ‘Abyei Aflame: An update from the field’, enough: the project to end genocide and crimes against humanity, 30 May. Retrieved 3 August 2008.
- ^ Arbitration Agreement between the Government of Sudan and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement/Army on Delimiting Abyei Area, 7 July 2008, http://www.pca-cpa.org/upload/files/Abyei%20Arbitration%20Agreement.pdf Archived 27 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "J:\Office Managers\Basic Documents English\2d ed\Revised\1STATENG.wpd" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 October 2011. Retrieved 6 December 2011.
- ^ "Abyei Arbitration". Pca-cpa.org. Archived from the original on 20 November 2011. Retrieved 6 December 2011.
- ^ The broadcasts of the Abyei Arbitration hearing are available on the PCA’s website: "Abyei Arbitration". Archived from the original on 20 November 2011. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ Final Award, 22 July 2009, "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 August 2009. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). The Award was accompanied by a map of the Abyei area as determined by the arbitration tribunal: "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 August 2009. Retrieved 22 July 2009.{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "New borders for Sudan oil region". BBC News. 22 July 2009. Archived from the original on 22 July 2009. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ Otterman, Sharon (22 July 2009). "Court Redraws Disputed Area in Sudan". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 July 2009.
- ^ Hamilton, Rebecca "How a Residency Dispute in One Key Town Could Lead Sudan Back to War", Christian Science Monitor, 3 November 2010, via Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting.
- ^ Al Jazeera (5 January 2011). "Tribal trouble in Sudan". ALJAZEERA. Archived from the original on 6 January 2011. Retrieved 7 January 2011.
- ^ a b BBC World News (22 May 2011). "Sudan: Abyei seizure by North 'act of war', says South". BBC. Archived from the original on 27 May 2011. Retrieved 22 May 2011.
- ^ a b James Copnall, BBC News, 23 May 2011
- ^ "North Sudan seizes disputed Abyei, thousands flee". Reuters. 22 May 2011. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- ^ BBC World News (25 May 2011). "Sudan's Abyei dispute: 'Shots fired' at UN helicopters". BBC. Archived from the original on 26 May 2011. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- ^ a b "Sudan appoints new chief administrator for Abyei area – Sudan Tribune: Plural news and views on Sudan". Sudan Tribune. Retrieved 6 December 2011.
- ^ "UPPER NILE STATE PROTESTS AGAINST ABYEI OCCUPATION". Sudan Catholic Radio Network. 27 May 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- ^ "Peaceful protest in Warrup State over takeover of Abyei". Miraya FM. 28 May 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- ^ F_404 (21 June 2011). "AU: Agreement on Abyei demilitarization done, more deals in works – People's Daily Online". People's Daily. Retrieved 6 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Resolution 1990 (2011)". United Nations. Retrieved 21 March 2017.
- ^ "Ethiopian peacekeepers to arrive in Abyei Friday". San Jose Mercury News. 14 July 2011. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ^ Ashine, Argaw (15 July 2011). "Ethiopian peacekeepers arrive in contested Abyei". Africa Review. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ^ "UNISFA condemns recent attacks in Abyei". UNmissions.org. 12 July 2017. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- ^ "Statement from UNISFA on the recent spate of attacks in Abyei". UNmissions.org. 18 October 2017. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- ^ "NCP And SPLM Signs Abyei Agreement in Addis Ababa". Gurtong.net. 23 June 2011. Retrieved 6 December 2011.
- ^ "Abyei Protocol Fact Sheet" (PDF). UNmissions.org. 24 February 2009. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- ^ "Abyei Administration Area Changes Name". Gurtong.net. 29 July 2015. Archived from the original on 13 February 2018. Retrieved 14 August 2016.
- ^ "Abyei chief confident in UNISFA security | Radio Tamazuj". Radio Tamazuj. Archived from the original on 4 April 2017. Retrieved 4 April 2017.
- ^ Angok, Daniel. "Abyei Residents Welcome New Chief Administrator". Gurtong.net. Retrieved 4 April 2017.
- ^ "South Sudan president sacks Abyei chief administrator - Sudan Tribune: Plural news and views on Sudan". www.sudantribune.com. Retrieved 4 April 2017.
- ^ "Kiir appoints governors for eight states". Radio Tamazuj. Retrieved 1 July 2020.
- ^ Hamilton, Rebecca "’Oil-rich’ Abyei: Time to update the shorthand?" Archived 14 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Christian Science Monitor, 3 November 2010, via Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting.
- ^ APS Review Downstream Trends 2007, ‘SUDAN: The oil sector’, www.entrepreneur.com, 29 October. Retrieved 5 March 2008.
- ^ USAID 2001, ‘Sudan: Oil and gas concession holders’ (map), University of Texas Library.
Further reading[edit]
- Douglas Johnson, 2008, "Why Abyei Matters, The Breaking Point of Sudan’s Comprehensive Peace Agreement?” in African Affairs, 107 (462), pp 1–19.
- Abraham, I. 2007, ‘South Sudan Abyei now or never’ Archived 28 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine, Sudan Tribune, 3 March. (Opinion piece.)
- Johnson, D. 2006, ‘Sudan's civil wars’ (video, filmed March, Bergen, Norway. (Brief discussion of underlying causes of conflict in Sudan.)
- Kristof, N. 2008, ‘Africa’s next slaughter’, New York Times, 2 March. Retrieved 4 March 2008. (Opinion piece concerning Abyei and the peace process.)
- UNDP 2005, "First Three of Eighteen Ongoing Development Projects Were Handed Over By UNDP to Abyei Communities" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 24 October 2007. (29.8 KB), United Nations Development Program Sudan, 29 November.
- Vall, M. 2008, ‘Abyei region divided over oil’, Al Jazeera English, 15 March. Retrieved 27 April 2008. (Video presentation hosted by YouTube.)
- Winter, R. 2008, ‘Sounding the alarm on Abyei’, enough: the project to end genocide and crimes against humanity, 17 April. Retrieved 5 May 2008.
- Winter, R. 2008, ‘Abyei aflame: An update from the field’, enough: the project to end genocide and crimes against humanity, 30 May. Retrieved 6 June 2008 (Describes May 2008 violence. Winter says that "the town of Abyei has ceased to exist".).


